Did You Know That About 2000 Thunderstorms
Severe Weather 101
Thunderstorm Nuts
Read more than nigh NSSL's thunderstorm enquiry here.
- What is a thunderstorm?
- A thunderstorm is a pelting shower during which you hear thunder. Since thunder comes from lightning, all thunderstorms have lightning.
- Why do I sometimes hear meteorologists apply the word "convection" when talking virtually thunderstorms?
- Commonly created by surface heating, convection is upward atmospheric motion that transports whatever is in the air along with it—peculiarly whatever moisture available in the air. A thunderstorm is the result of convection.
- What is a severe thunderstorm?
- A thunderstorm is classified as "severe" when it contains one or more of the following: hail 1 inch or greater, winds gusting in backlog of l knots (57.5 mph), or a tornado.
- How many thunderstorms are there?
- Worldwide, at that place are an estimated 16 million thunderstorms each year, and at any given moment, there are roughly 2,000 thunderstorms in progress. At that place are about 100,000 thunderstorms each year in the U.Due south. alone. About x% of these reach severe levels.
- When are thunderstorms most probable?
- Thunderstorms are near likely in the spring and summer months and during the afternoon and evening hours, but they can occur twelvemonth-round and at all hours.
Along the Gulf Coast and across the southeastern and western states, nigh thunderstorms occur during the afternoon. Thunderstorms frequently occur in the late afternoon and at night in the Plains states.
- What kinds of damage tin can thunderstorms cause?
- Many hazardous weather events are associated with thunderstorms. Under the correct conditions, rainfall from thunderstorms causes flash flooding, killing more people each year than hurricanes, tornadoes or lightning. Lightning is responsible for many fires around the earth each year, and causes fatalities. Hail up to the size of softballs damages cars and windows, and kills livestock caught out in the open. Potent (up to more than 120 mph) directly-line winds associated with thunderstorms knock down trees, ability lines and mobile homes. Tornadoes (with winds up to near 300 mph) tin can destroy all only the best-built man-fabricated structures.
- Where are severe thunderstorms most common?
- The greatest severe atmospheric condition threat in the U.S. extends from Texas to southern Minnesota. Simply, no place in the United States is completely safe from the threat of severe weather.
- What is the difference betwixt a Severe Thunderstorm WATCH and a Astringent Thunderstorm Alarm?
- A Severe Thunderstorm WATCH is issued by the NOAA Storm Prediction Center meteorologists who are watching the conditions 24/7 across the entire U.S. for weather weather that are favorable for severe thunderstorms. A watch can encompass parts of a country or several states. Scout and prepare for severe weather condition and stay tuned to NOAA Atmospheric condition Radio to know when warnings are issued.
A Astringent Thunderstorm Warning is issued by your local NOAA National Weather Service Forecast Office meteorologists who watch a designated surface area 24/7 for severe weather that has been reported by spotters or indicated by radar. Warnings mean there is a serious threat to life and holding to those in the path of the storm. ACT now to notice condom shelter! A warning tin cover parts of counties or several counties in the path of danger.
- How does a thunderstorm form?
- 3 bones ingredients are required for a thunderstorm to form: moisture, rising unstable air (air that keeps rise when given a nudge), and a lifting mechanism to provide the "nudge."
The dominicus heats the surface of the world, which warms the air above it. If this warm surface air is forced to ascent—hills or mountains, or areas where warm/cold or wet/dry air crash-land together tin can cause rise movement—it will go along to rise every bit long as it weighs less and stays warmer than the air effectually information technology.
Equally the air rises, information technology transfers estrus from the surface of the earth to the upper levels of the atmosphere (the process of convection). The water vapor it contains begins to cool, releases the rut, condenses and forms a cloud. The cloud eventually grows upwardly into areas where the temperature is below freezing.
As a storm rises into freezing air, dissimilar types of ice particles can be created from freezing liquid drops. The ice particles tin can grow by condensing vapor (like frost) and by collecting smaller liquid drops that haven't frozen yet (a country chosen "supercooled"). When two water ice particles collide, they unremarkably bounce off each other, just one particle can rip off a little bit of ice from the other one and grab some electric accuse. Lots of these collisions build up large regions of electric charges to cause a commodities of lightning, which creates the sound waves we hear every bit thunder.
- The Thunderstorm Life Bicycle
- Thunderstorms accept three stages in their life cycle: The developing stage, the mature stage, and the dissipating stage. The developing stage of a thunderstorm is marked by a cumulus cloud that is being pushed upward past a rising cavalcade of air (updraft). The cumulus cloud soon looks like a tower (chosen towering cumulus) as the updraft continues to develop. There is fiddling to no rain during this stage merely occasional lightning. The thunderstorm enters the mature stage when the updraft continues to feed the storm, only precipitation begins to fall out of the tempest, creating a downdraft (a column of air pushing downward). When the downdraft and rain-cooled air spreads out forth the footing it forms a gust forepart, or a line of gusty winds. The mature stage is the about likely time for hail, heavy rain, frequent lightning, strong winds, and tornadoes. Eventually, a big amount of precipitation is produced and the updraft is overcome by the downdraft beginning the dissipating stage. At the ground, the gust front moves out a long altitude from the storm and cuts off the warm moist air that was feeding the thunderstorm. Rainfall decreases in intensity, but lightning remains a danger.
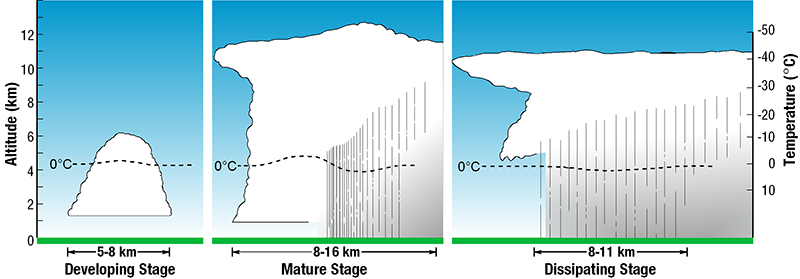
Life cycle of a thunderstorm [+]
- What does a thunderstorm look similar?
- Thunderstorms can expect like tall heads of cauliflower or they can have "anvils." An anvil is the flat deject formation at the top of the storm. An anvil forms when the updraft (warm air rising) has reached a point where the surrounding air is about the same temperature or fifty-fifty warmer. The cloud growth abruptly stops and flattens out to take the shape of an anvil.
Source: https://www.nssl.noaa.gov/education/svrwx101/thunderstorms/
0 Response to "Did You Know That About 2000 Thunderstorms"
Post a Comment